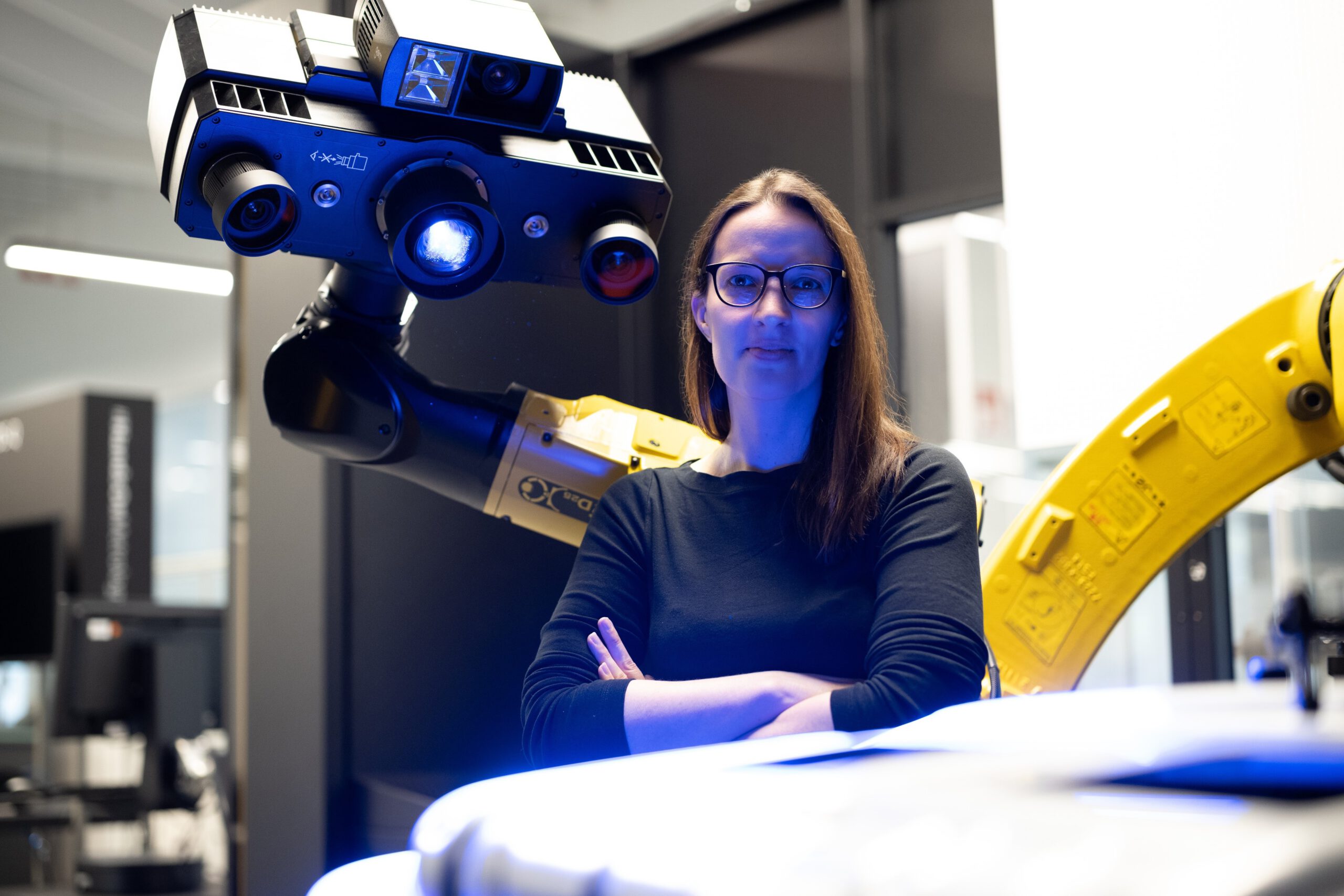
Have you ever wondered how we can measure the physical properties of objects without even touching them? Well, get ready to discover the magic of optical metrology!
What is optical metrology?
It is a technique that uses light to measure different physical properties of objects. It helps us gather information about things like distance, shape, size, and surface roughness. This method finds applications in various fields, such as manufacturing, engineering, biology, and medicine.
How does optical metrology work?
It works by interacting light with the object we want to measure. We analyze how the light behaves when it reflects, refracts, transmits, or gets absorbed by the object. There are different methods we can use, like creating interference patterns with multiple light beams, analyzing how light scatters off a rough surface, or projecting patterns onto the object to create a 3D map of its shape.
Where is optical metrology used?
Optical metrology has many practical applications, including:
- Manufacturing and Engineering: It helps ensure the quality and accuracy of parts and components by measuring dimensions, surface roughness, and monitoring surface treatments.
- Biomedical and Life Sciences: It is used to study cells, tissues, and organs. It helps measure their size, shape, and surface roughness.
- Archaeology and Conservation: It accurately measures and documents cultural heritage objects. It assists in creating 3D models of artifacts and monitoring changes in the condition of historical buildings and monuments.
- Aerospace and Defense: It is utilized to measure the shape and surface quality of parts and components, such as mirrors, lenses, and radar-absorbing materials.
Advantages and disadvantages of optical metrology
Advantages
- Non-contact measurement technique, minimizing the risk of object damage.
- Provides accurate measurements, making it suitable for tasks that require precision.
- Quick measurements, making it valuable for time-sensitive applications.
Disadvantages
- Sensitive to environmental changes like temperature, humidity, and vibrations, which can affect measurement accuracy.
- Limited range depending on the specific method used, making it challenging to measure large objects or surfaces.
- Equipment and methods can be expensive, which may limit accessibility for some applications.
In conclusion, optical metrology is a useful technique that uses light to measure physical properties of objects. It has a wide range of applications in various industries and fields. Although it has limitations, efforts are made to overcome these challenges and maximize the advantages of optical metrology, making it an important tool for many applications.
PS: It is also one of the fields I am working in at Zeiss Group.
Feature photo: Manfred Stich, Carl Zeiss AG
For further information or if you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact me.